Position, rotation, scale: Transforming entities
Transforming SFML entities
All SFML classes (sprites, text, shapes) use the same interface for transformations: Transformable. This base class provides a simple API to move, rotate and scale your entities. It doesn't provide maximum flexibility, but instead defines an interface which is easy to understand and to use, and which covers 99% of all use cases -- for the remaining 1%, see the last chapters.
Transformable (and all its derived classes) defines four properties: position, rotation, scale and origin. They all have their respective getters and setters. These transformation components are all independent of one another: If you want to change the orientation of the entity, you just have to set its rotation property, you don't have to care about the current position and scale.
Position
The position is the... position of the entity in the 2D world. I don't think it needs more explanation :).
import sfml.graphics.Text
import sfml.system.Vector2
val entity: Text = ???
// 'entity' can be a Sprite, a Text or any other transformable class
// set the absolute position of the entity
entity.position = (10, 50)
// move the entity relatively to its current position
entity.move(5, 5)
// retrieve the absolute position of the entity
val position: Vector2[Float] = entity.position // = (15, 55)
By default, entities are positioned relative to their top-left corner. We'll see how to change that with the 'origin' property later.
Rotation
The rotation is the orientation of the entity in the 2D world. It is defined in degrees, in clockwise order (because the Y axis is pointing down in SFML).
import sfml.graphics.Text
import sfml.system.{Angle, Vector2, deg}
val entity: Text = ???
// 'entity' can be a Sprite, a Text or any other transformable class
// set the absolute rotation of the entity
entity.rotation = 45.deg
// rotate the entity relatively to its current orientation
entity.rotate(10.deg)
// retrieve the absolute position of the entity
val rotation: Angle = entity.rotation // = 55 degrees
Note that SFML always returns an angle in range [0, 360) when you fetch the rotation.
As with the position, the rotation is performed around the top-left corner by default, but this can be changed by setting the origin.
Scale
The scale factor allows the entity to be resized. The default scale is 1. Setting it to a value less than 1 makes the entity smaller, greater than 1 makes it bigger. Negative scale values are also allowed, so that you can mirror the entity.
import sfml.graphics.Text
import sfml.system.Vector2
val entity: Text = ???
// 'entity' can be a Sprite, a Text or any other transformable class
// set the absolute scale of the entity
entity.scale = (4.0f, 1.6f)
// scale the entity relatively to its current scale
entity.scale(0.5f, 0.5f)
// retrieve the absolute scale of the entity
val scale: Vector2[Float] = entity.scale // = (2.0, 0.8)
Origin
The origin is the center point of the three other transformations. The entity's position is the position of its origin, its rotation is performed around the origin, and the scale is applied relative to the origin as well. By default, it is the top-left corner of the entity (point (0, 0)), but you can set it to the center of the entity, or any other corner of the entity for example.
To keep things simple, there's only a single origin for all three transformation components. This means that you can't position an entity relative to its top-left corner while rotating it around its center for example. If you need to do such things, have a look at the next chapters.
import sfml.graphics.Text
import sfml.system.Vector2
val entity: Text = ???
// 'entity' can be a Sprite, a Text or any other transformable class
// set the origin of the entity
entity.origin = (10, 20)
// retrieve the origin of the entity
val origin: Vector2[Float] = entity.origin // = (2.0, 0.8)
Note that changing the origin also changes where the entity is drawn on screen, even though its position property hasn't changed. If you don't understand why, read this tutorial one more time!
Transforming your own classes
Transformable is not only made for SFML classes, it can also be a base (or member) of your own classes.
import sfml.graphics.Transformable
import sfml.system.deg
class MyGraphicalEntity extends Transformable(using Transformable.ctor())
val entity = MyGraphicalEntity()
entity.position = (10, 30)
entity.rotation = 110.deg
entity.scale = (0.5f, 0.2f)
To retrieve the final transform of the entity (commonly needed when drawing it), use transform. This returns a Transform object. See below for an explanation about it, and how to use it to transform an SFML entity.
If you don't need/want the complete set of functions provided by the Transformable interface, don't hesitate to simply use it as a member instead and provide your own functions on top of it. It is not a trait, so it is possible to instantiate it instead of only being able to use it as a base class.
Custom transforms
The [Transformable] class is easy to use, but it is also limited. Some users might need more flexibility. They might need to specify a final transformation as a custom combination of individual transformations. For these users, a lower-level class is available: Transform. It is nothing more than a 3x3 matrix, so it can represent any transformation in 2D space.
There are many ways to construct a [Transform]:
- by using the predefined functions for the most common transformations (translation, rotation, scale)
- by combining two transforms
- by specifying its 9 elements directly
Here are a few examples:
import sfml.graphics.Transform
import sfml.system.deg
// the identity transform (does nothing)
val t1 = Transform.Identity()
// a rotation transform
val t2 = Transform().rotate(45.deg)
// a custom matrix
val t3 = Transform(
2.0f, 0.0f, 20.0f,
0.0f, 1.0f, 50.0f,
0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f
)
// a combined transform
val t4 = t1 * t2 * t3
You can apply several predefined transformations to the same transform as well. They will all be combined sequentially. Note that transforming an object by combining multiple transformations is equivalent to applying each operation in reverse order. The last operation (here scale) is applied first, and will be affected by operations above it in code (second would be translate(-10, 50), for example).
import sfml.graphics.Transform
import sfml.system.deg
val t = Transform()
t.translate((10, 100))
t.rotate(90.deg)
t.translate((-10, 50))
t.scale((0.5f, 0.75f))
Back to the point: How can a custom transform be applied to a graphical entity? Simple: Pass it to the draw function through RenderStates.
import sfml.graphics.{RenderStates, RenderWindow, Transform, Sprite}
import sfml.window.VideoMode
val window = RenderWindow(VideoMode((800, 600)), "My window")
val entity: Sprite = ???
val transform = Transform()
window.draw(entity, RenderStates(transform))
If your entity is a Transformable (sprite, text), which contains its own internal transform, both the internal and the passed transform are combined to produce the final transform.
Bounding boxes
After transforming entities and drawing them, you might want to perform some computations using them e.g. checking for collisions.
SFML entities can give you their bounding box. The bounding box is the minimal rectangle that contains all points belonging to the entity, with sides aligned to the X and Y axes.
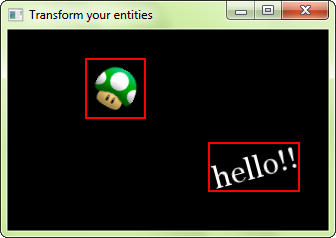
The bounding box is very useful when implementing collision detection: Checks against a point or another axis-aligned rectangle can be done very quickly, and its area is close enough to that of the real entity to provide a good approximation.
import sfml.Immutable
import sfml.graphics.{Rect, Sprite}
import sfml.system.Vector2
val entity: Sprite = ???
// get the bounding box of the entity
val boundingBox: Immutable[Rect[Float]] = entity.globalBounds
// check collision with a point
val point: Vector2[Float] = (100f, 200f)
if boundingBox.contains(point) then
() // collision!
// check collision with another box (like the bounding box of another entity)
val otherBox: Rect[Float] = ((100f, 200f), (50f, 50f))
if boundingBox.findIntersection(otherBox).isDefined then
() // collision!
The accessor is named globalBounds because it returns the bounding box of the entity in the global coordinate system, i.e. after all of its transformations (position, rotation, scale) have been applied.
There's another function that returns the bounding box of the entity in its local coordinate system (before its transformations are applied): localBounds. This function can be used to get the initial size of an entity, for example, or to perform more specific calculations.